
tumor in sinus maxillaris dexter a photo on Flickriver
An understanding of the fundamental principles of the development, physiology, anatomy and relationships of the maxillary sinus as depicted by multi-modality imaging is essential for radiologists reporting imaging involving the paranasal sinuses and midface. Keywords: Maxillary Sinus, Dentition - Anatomy, Physiology, Diagnostic Imaging.
LocalIzed AmyloId Tumor Of The MaxIllary SInus Selcuk Medical Journal
The maxillary sinus (MS), one of the paranasal sinuses first identified by ancient Egyptians, has been well studied, especially its structure, vascular anatomy, and relationship with the teeth [ 1 ]. Since the introduction of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) into clinical practice, sinus floor augmentation (SFA) has become more popular.

Figuur 1 CTscan van patiënt a ter hoogte van de sinus maxillaris. In... Download Scientific
Doctors also use a cancer's stage when talking about survival statistics. The earliest stage of nasal cavity and paranasal sinus cancers is stage 0, also known as carcinoma in situ (CIS). The other stages range from I (1) through IV (4). Some stages are split further, using capital letters (A, B, etc.).
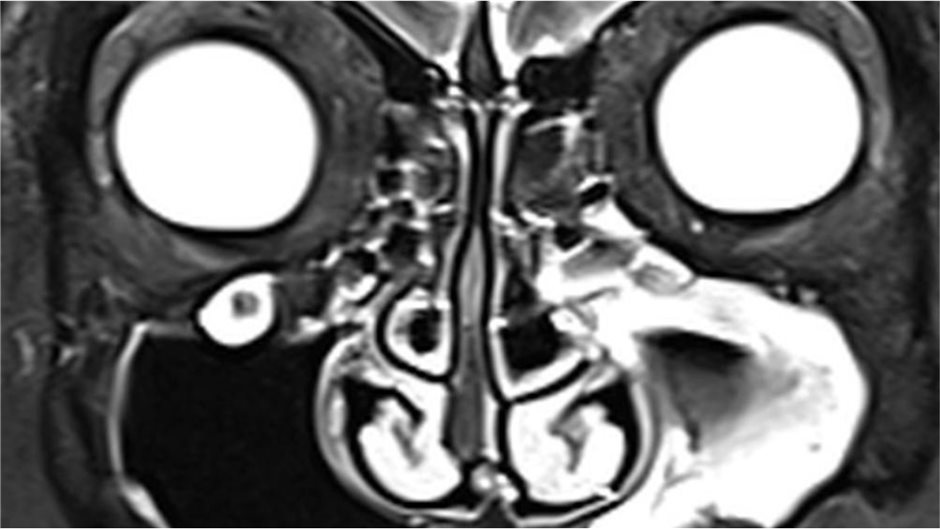
MRT einer Sinusitis maxillaris
Gross anatomy. Described as a pyramid, the maxillary sinuses have a base on the lateral border of the nose, with the apex pointing towards the zygomatic process of the maxilla. The floor is formed by the alveolar process of the maxilla. The roof is the orbital floor. The posterior wall forms the anterior border of the pterygopalatine fossa.

De sinus maxillaris en dentogene cysten NTvG
Tumor restricted to any 1 subsite, with or without bony invasion. T2. Tumor invading 2 subsites in a single region or extending to involve an adjacent region within the nasoethmoidal complex, with or without bony invasion. T3. Tumor extends to invade the medial wall or floor of the orbit, maxillary sinus, palate, or cribriform plate. T4
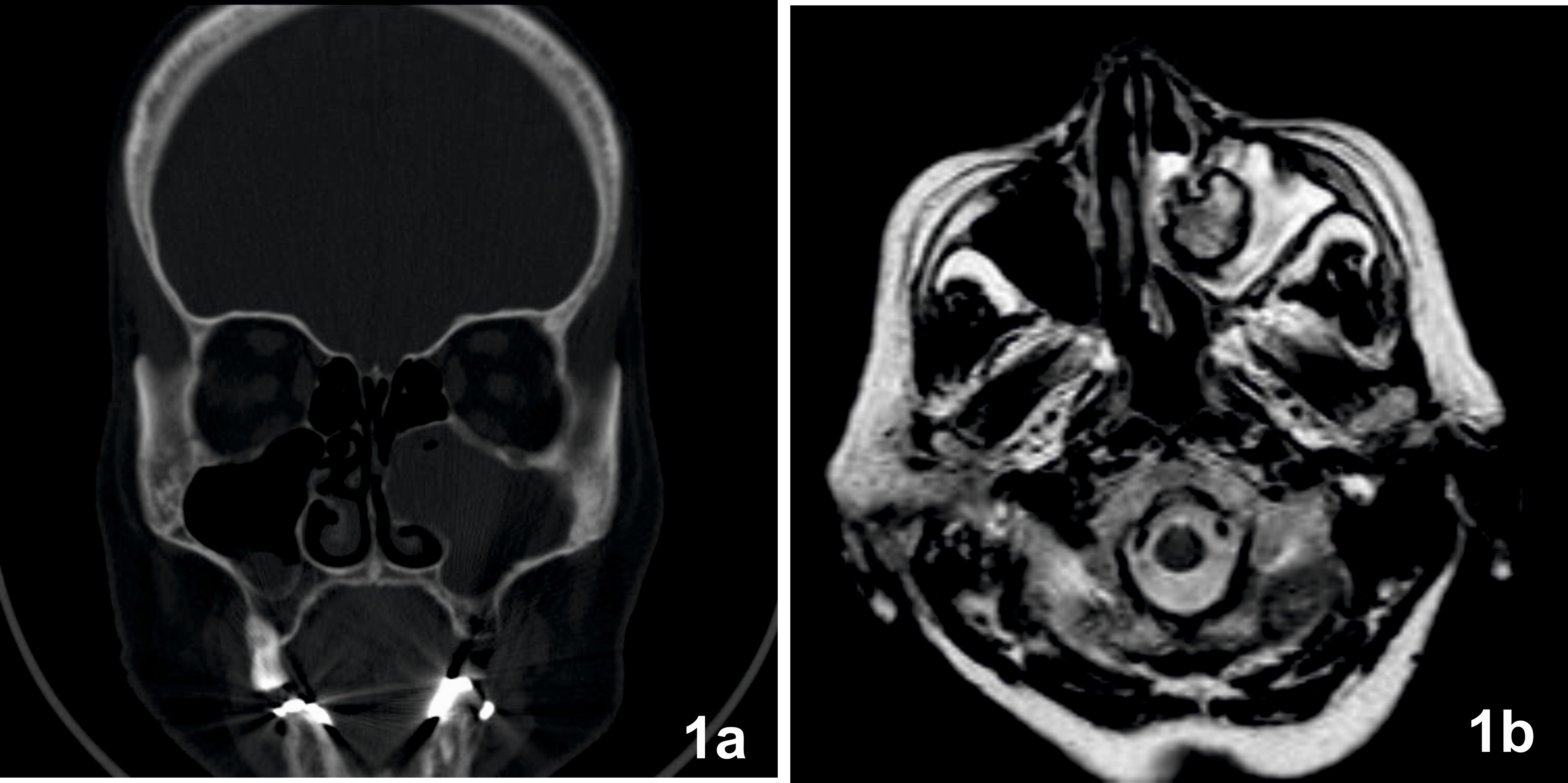
Reports Free FullText A Case Report of a Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Maxillary Sinus
There are 3 grades of maxillary sinus cancer: grade 1 (low grade) - the cancer cells look very much like the normal maxillary sinus cells. grade 2 (intermediate grade) - the cancer cells look slightly like normal maxillary sinus cells. grade 3 (high grade) - the cancer cells look very abnormal and very little like normal maxillary sinus cells.

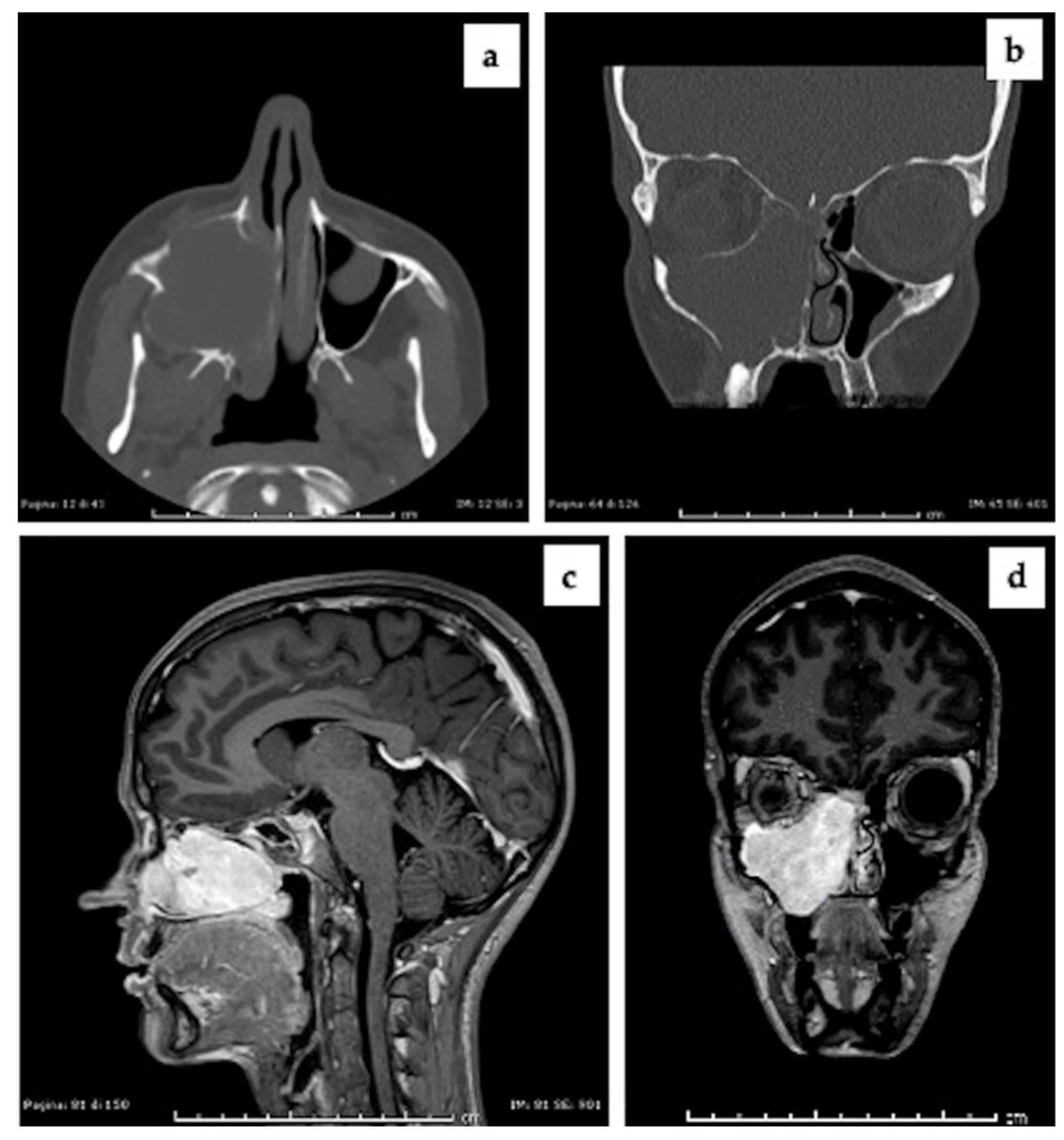
Immature Teratoma of the Maxillary Sinus A Rare Pediatric Tumor Pediatric Cancer JAMA
A doctor will conduct tests to determine the stage of maxillary sinus cancer, which is then used develop an appropriate treatment plan. The following stages are used for maxillary sinus cancer: Stages 0 maxillary sinus cancer. Stages 1 maxillary sinus cancer. Stages 2 maxillary sinus cancer. Stages 3 maxillary sinus cancer.
CT vs. MRI cyst in sinus maxillaris a photo on Flickriver
Maxillary cancer is often diagnosed at an advanced stage and in most cases requires a multimodal approach. Perineural and lymphovascular invasion are frequent and have a different impact on prognosis and topographical extension of the tumor.. Malignant tumors of the maxillary sinus: Prognostic impact of neurovascular invasion in a series of.
Cureus Sinonasal NUTMidline Carcinoma A Multimodality Approach to Diagnosis, Staging and
Maxillary Sinus. Maxillary sinuses, the largest of the paranasal sinuses, are pyramid-shaped cavities located in the maxillae. The base of the maxillary sinus forms the inferior part of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity. The roof of the maxillary sinus is formed by the floor of the orbit, which contains the infraorbital canal, and the floor.

Maxillary Sinus Ameloblastoma Presented With Only Sinus Pain
This type of tumor is rare. Less than one-half percent of all diagnosed cancers are cancerous sinus tumors, and not all sinus tumors are cancerous. However, treatment is usually needed because.

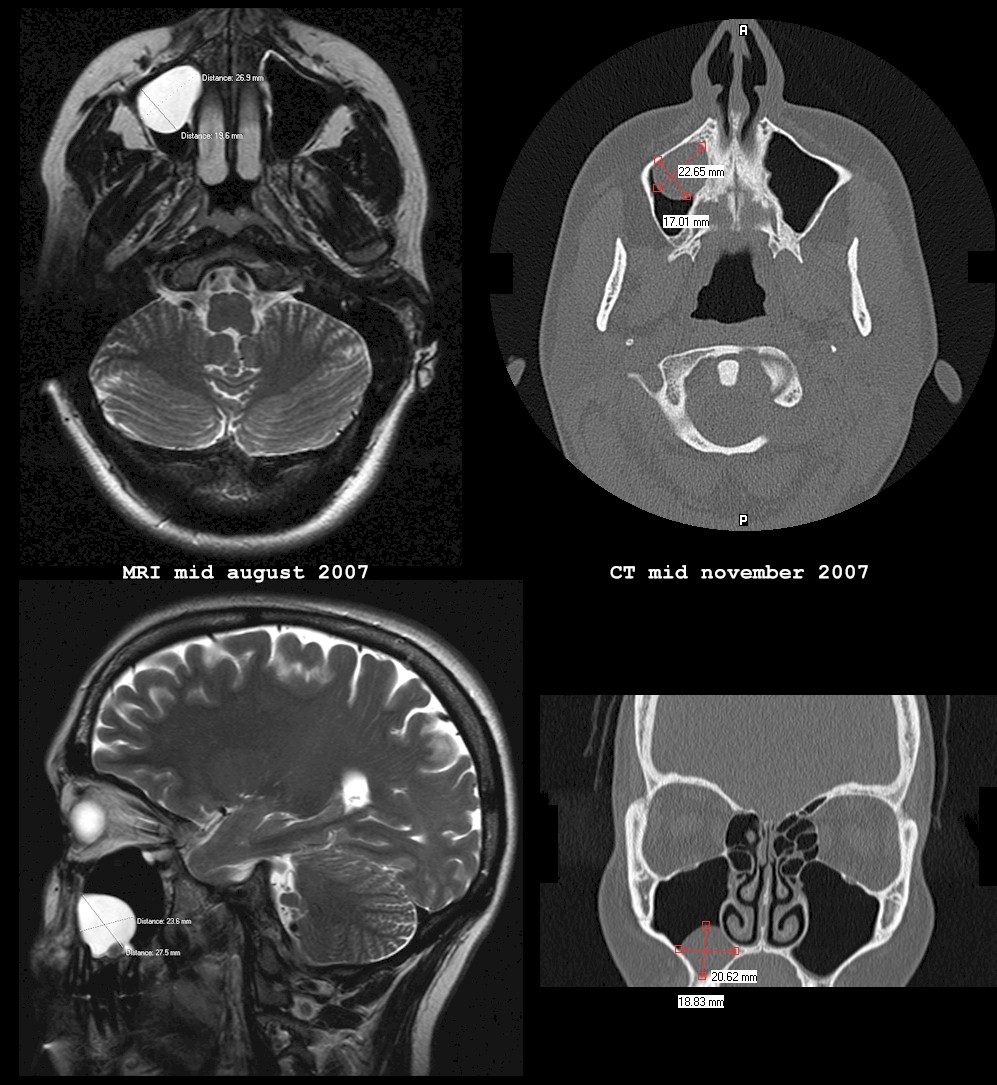
CT 3 cm diameter, oval hypodense tumor in right maxillary sinus. Download Scientific Diagram
radiopacity caused may obscure the image of the sinus or may actually encroach on the sinus VII. TUMORS OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS. Benign and malignant tumors may have an origin within or may encroach upon the sinus. The dental radiograph plays an important role in early recognition of these lesions at a time when they are amenable to treatment.
MUCOUS RETENTION CYSTS OF MAXILLARY SINUS
Primary tumor (T) TX: primary tumor cannot be assessed; Tis: carcinoma in situ; T1: tumor limited to maxillary sinus mucosa (no bone erosion/destruction); T2: tumor with bone erosion/destruction, including extension into hard palate and/or middle meatus, excluding structures in a higher T category; T3: tumor invades any of the following:. bone of posterior wall of maxillary sinus

Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary sinus Report of two cases in association with
Signs and symptoms of sinus cancer often occur only on one side and include: Nasal congestion and stuffiness that doesn't get better or even worsens. Numbness or pain in your upper cheek or above or below the eyes. Blockage on one side of your nose, frequent nosebleeds, or mucus running from the nose. Postnasal drip (mucus draining into the.

(PDF) Maxillary Sinus Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumors A Review and Case Report
nosebleeds. headaches. mucus with blood coming out of your nose. a decrease in your sense of smell. feeling like one side of your nose is blocked. mucus running down your throat. Symptoms of more.

Panoramic radiography is of limited value in the evaluation of maxillary sinus disease Oral
Introduction. Maxillary sinus cancer is a relatively rare neoplasm with an incidence representing a small percentage (0.2%) of human malignant tumors and only 1.5% of all head and neck malignant neoplasms [].Asian countries report a very high incidence of maxillary sinus carcinoma, which makes it important for us to raise general awareness among oral stomatologists [].
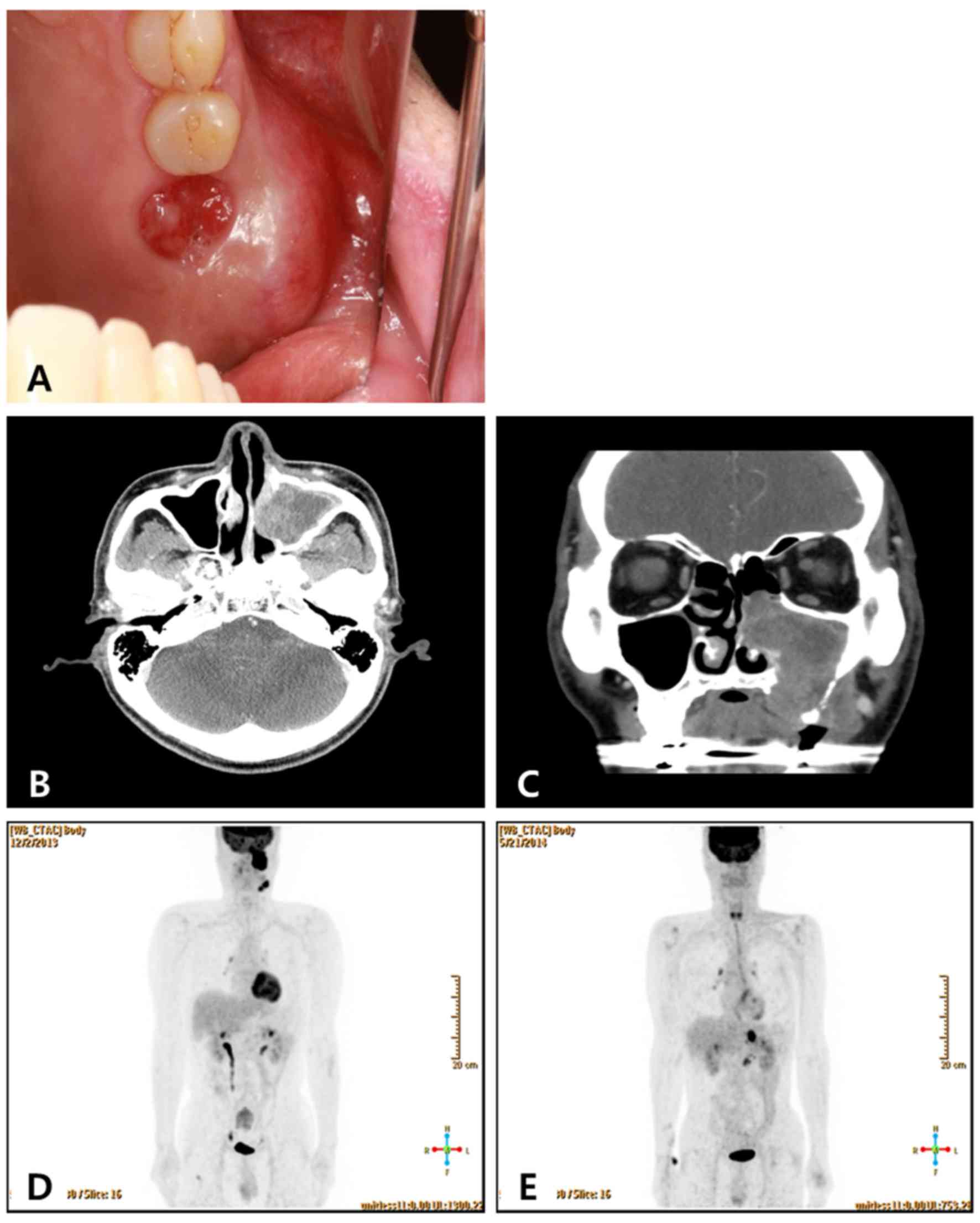
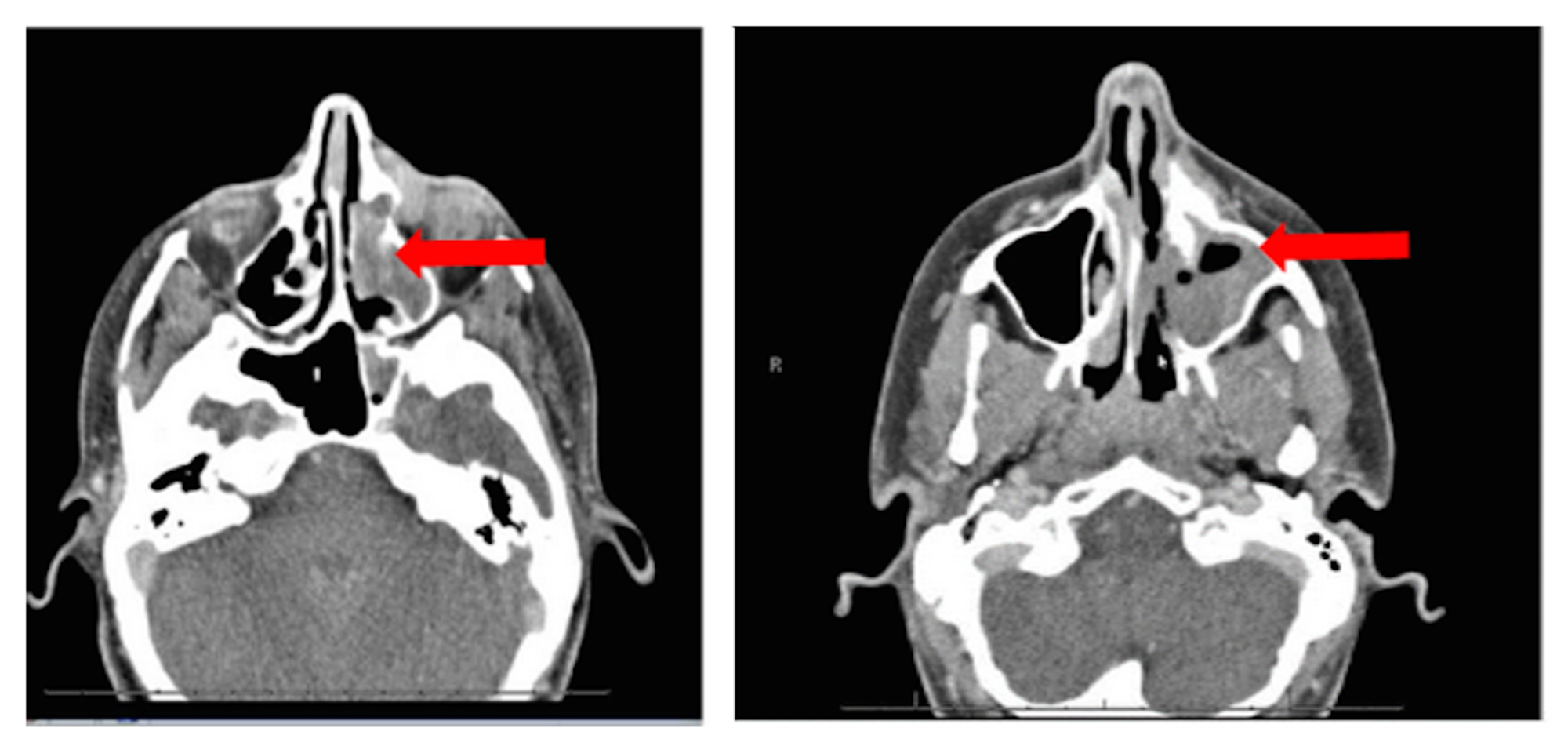
Recurrent maxillary sinus cancer with only adrenal metastasis
The maxillary ostium (hiatus maxillaris), tough wide in the disarticulated maxilla, is greatly reduced in size in anatomical conditions, due to several complex spatial interactions with other bony and mucous structures.. New tumor entities in the 4th edition of the World Health Organization classification of head and neck tumors: nasal.